Difference between revisions of "HTAP Report, Sub-Chap. 6 - Data/Info System"
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== Misc Stuff== | == Misc Stuff== | ||
| − | + | Recent developments in air quality monitoring, modeling and information technologies offer outstanding | |
| − | + | opportunities to fulfill the information needs for the HTAP integration effort. The data from surface-based air pollution monitoring networks now routinely provide spatio-temporal and chemical patterns of ozone and PM. Satellite | |
| − | opportunities to fulfill the information needs for the | + | sensors with global coverage and kilometer-scale spatial resolution now provide real-time snapshots which depict the pattern of industrial haze, smoke and dust in stunning detail. The ‘terabytes’ of data from these surface and remote sensors can now be stored, processed and delivered in near-real time. The instantaneous ‘horizontal’ diffusion of information via the Internet now permits, in principle, the delivery of the right information to the right people at the right place and time. Standardized computer-computer communication languages and Service-Oriented Architectures(SOA) now facilitate the flexible access, quality assurance and processing of raw data into high-grade ‘actionable’ knowledge suitable for HTAP policy decissions. Last but not least, the World Wide Web has opened the way to generous sharing of data and tools leading to collaborative analysis and virtual workgroups. Nevertheless, air quality data analyses and data model integration face significant hurdles. |
| − | The data from surface-based air pollution monitoring networks now | ||
| − | spatio-temporal and chemical patterns | ||
| − | sensors with global coverage and kilometer-scale spatial resolution now provide real-time | ||
| − | snapshots which depict the pattern of haze, smoke and dust in stunning detail. The ‘terabytes’ of | ||
| − | data from these surface and remote sensors can now be stored, processed and delivered in | ||
| − | time. The instantaneous ‘horizontal’ diffusion of information via the Internet now permits, in | ||
| − | principle, the delivery of the right information to the right people at the right place and time. | ||
| − | Standardized computer-computer communication languages and Service-Oriented Architectures | ||
| − | (SOA) now facilitate the flexible processing of raw data into high-grade ‘actionable’ knowledge. | ||
| − | Last but not least, the World Wide Web has opened the way to generous sharing of data and | ||
| − | tools leading to | ||
| − | Nevertheless, air quality | ||
The new developments introduced a new set of problems. The “data deluge” problem is | The new developments introduced a new set of problems. The “data deluge” problem is | ||
| Line 68: | Line 56: | ||
but much more could be done. The current challenge is to incorporate such support into the air | but much more could be done. The current challenge is to incorporate such support into the air | ||
quality management process in a more regular and robust way. | quality management process in a more regular and robust way. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Integration of Observations and Emissions== | ==Integration of Observations and Emissions== | ||
Revision as of 20:49, April 11, 2007
< Back to Integrated Global Dataset on ESIP wiki
Fragments for Chapter 6. Integration of Observations, Emissions and Modeling
This wiki page is inteded to be the collaborative workspace for Task Force members interested in the HTAP Information System development, implementation and use. The contents can be freely edited by anyone who is logged in. Comments and feedback can also be sent by email to rhusar@me.wustl.edu. The content of this page is is on the Information System that supposts Chapter 6. The subsections are action-oriented.
From Oct 2006 Prospectus: This chapter (Chapter 6: Integration of Observations, Emissions and Modeling.) will discuss the need to integrate information from observations, models, and emissions inventories to better understand intercontinental transport. A draft HTAP Report Chap. 6 - Jan 07 Outline is also on this wiki.
Misc Stuff
Recent developments in air quality monitoring, modeling and information technologies offer outstanding opportunities to fulfill the information needs for the HTAP integration effort. The data from surface-based air pollution monitoring networks now routinely provide spatio-temporal and chemical patterns of ozone and PM. Satellite sensors with global coverage and kilometer-scale spatial resolution now provide real-time snapshots which depict the pattern of industrial haze, smoke and dust in stunning detail. The ‘terabytes’ of data from these surface and remote sensors can now be stored, processed and delivered in near-real time. The instantaneous ‘horizontal’ diffusion of information via the Internet now permits, in principle, the delivery of the right information to the right people at the right place and time. Standardized computer-computer communication languages and Service-Oriented Architectures(SOA) now facilitate the flexible access, quality assurance and processing of raw data into high-grade ‘actionable’ knowledge suitable for HTAP policy decissions. Last but not least, the World Wide Web has opened the way to generous sharing of data and tools leading to collaborative analysis and virtual workgroups. Nevertheless, air quality data analyses and data model integration face significant hurdles.
The new developments introduced a new set of problems. The “data deluge” problem is especially acute for analysts interest in aerosol pollution, since aerosols are so inherently complex and since there are so many different kinds of relevant data – from extensive, new surface-based monitoring networks, meteorological and aerosol forecast models, satellite imagery and associated data products, etc.
In this brief report we present DataFed, an infrastructure for real-time integration and web-based delivery of distributed monitoring data. Next we highlight FASTNET, a recent application project built on the DataFed infrastructure, which utilizes real-time and historical monitoring data for the collaborative study of major aerosol events.
DataFed is not a centrally planned and maintained data system but a facility to harness the emerging resources by powerful dynamic data integration technologies and through a collaborative federation philosophy.
The key roles of the federation infrastructure are to (1) facilitate registration of the distributed data in a user-accessible catalog; (2) ensure data interoperability based on physical dimensions of space and time; (3) provide a set of basic tools for data exploration and analysis. The federated datasets can be queried, by simply specifying a latitude-longitude window for spatial views, time range for time views, etc. This universal access is accomplished by ‘wrapping’ the heterogeneous data, a process that turns data access into a standardized web service, callable through well-defined Internet protocols.
The result of this ‘wrapping’ process is an array of homogeneous, virtual datasets that can be queried by spatial and temporal attributes and processed into higher-grade data products. The Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) of DataFed is used to build web-applications by connecting the web service components (e.g. services for data access, transformation, fusion, rendering, etc.) in Lego-like assembly. The generic web-tools created in this fashion include catalogs for data discovery, browsers for spatial-temporal exploration, multi-view consoles, animators, multi-layer overlays, etc.(Figure 2).
Recent developments in surface and satellite sensing along with new information technologies now allow real-time, ‘just-in-time’ data analysis for the characterization and partial explanation of the of major air pollution events as well as more in-depth post-analysis, integration and fusion can also be performed using the federated historical data resources and tools. By making available many spatio-temporal data sources through a single web interface and in a consistent format, the DataFed tools allow anyone to view, process, overlay, and display many types of data to gain insight to atmospheric physical and chemical processes. A goal of the current effort is to encourage use of these tools by a broad community of air pollution researchers and analysts, so that a growing group of empowered analysts may soon enhance the rate at which our collective knowledge of air pollution evolves. In recent years, such agile analyses have provided occasional real-time support to the air quality managers and to the public but much more could be done. The current challenge is to incorporate such support into the air quality management process in a more regular and robust way.
Integration of Observations and Emissions
A key early recommendation was to emphasize the integration of current and emerging data/information systems. The ultimate goal of that data system is to assemble for HTAP an appropriate set of observations, with known quality and representativeness, and to facilitate the integration and fusion of observations with models.
Sensing revolution.. from dataFed paper
Data Selection Criteria
Monitoring data for atmospheric constituents are now available from a variety of sources, not all of which are suitable for the integrated HTAP data set. Given the limited scope and resources of HTAP, it will be necessary to select a subset of the available observational data that would be most appropriate for the preparation of the 2009 assessment. A set of criteria for the data selection is given below.
- The suitability criteria may include the measured parameters, their spatial extent and coverage density, as well as the time range and sampling frequency with major emphasis on data quality (defined as???).
- The compilation of the global integrated data sets should initially focus on PM and ozone, including the gaseous precursors.
- Subsequent data collaction should also include observations on atmospheric mercury and persistent organic pollutants (POPS).
- In order to cover hemispheric transport of air pollutants the data set system should accept and utilize data from outside the geographical scope of EMEP.
- The data gathering should begin the compilation using the of existing databases in Europe (RETRO, TRADEOFF, QUANTIFY, CRATE, AEROCOM) and virtual federated systems in the US (DataFed, Giovanni and others).
- TF data integration should also contribute to and benefit from other ongoing data integration efforts to integrate the global data resources, most notably, with ACCENT project in Europe, and similar efforts in the US.
- Special emphasis should be placed on the collection of suitable vertical profiles from aircraft measurements as well as from surface and space-borne lidars.
The evaluation of suitabile observational data sets for model validation and fusion will require close interaction between the modeling and observational communities. An wiki workspace for open collaborative evaluation of different datasets is desirebale.
Homogenize the data into an interoperable dataset
The primary goal of the data system is to allow the integration of observational emission and model data. The model evaluation requires that both the observations and if possible the emissions are fixed. For this reason it is desirable to prepare an integrated observational database to which the various model implementations can be compared to. On one hand, the integrated data set should be as inclusive as possible. On the other hand, such a goal needs to be tempered by many limitations that preclude a broad, inclusive data integration
The proposed HTAP data system will be a hybrid combination of both distributed and fixed components as illustrated schematically in Figure ??. Both the data providers as well as the HTAP analysts-users will be distributed. However, they will be connected through an integrated HTAP database which should be a stable, virtually fixed database. The section below describes the main component of this distributed data system.
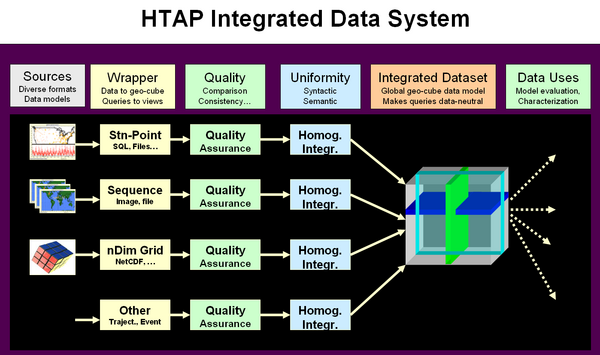
The HTAP integrated data system has to perform two major functions. The primary function is to facilitate the creation of an integrated data set suitable for model evaluation and pollutant characterization. The multiple steps that are required for this functionality are shown on the left. The sequence of operations can be viewed as a value chain that transform the raw input data into a highly organized integrated data set. Since these value adding steps have to be performed for each candidate data set the operations can be performed in sequence following the rules of data flow programming. For true quality assurance and for data homogenization the data flow channels for individual data sets need to be evaluated in the context of other data.
The operations that prepare the integrated data set can be viewed as services that operate on the data stream using the principles of modern Service Oriented Architecure (SOA). Each of the services with its clearly defined functionality and firmly specified service interface. In principle, the standards-based interface allows a connection of service chains using formal work flow software. The main benefit of service oriented architecture is that allows the building of agile application programs that can respond to changes in the data input conditions as well as the output requirements. The service oriented software architecture is an implementation of the System of Systems approach. Furthermore, since each of the services can be operated by autonomous providers and the "system" that implements the service is behind the service interfece. In other words, following the SOA approach, not only the data providers are distributed but also the processing services as well. This flexible approach to distributed computing allows the distribution of labor (chain of services) in many different configurations. For instance, wrapping the existing data with standards based interfaces for data access can be performed for an entire cluster of data. This is the approach taken in the federated data system DataFed. Given a standard interface to a variety of data sets, the Quality Assurance service can be performed by another srvice provider that is seamlesly connected to the data access mediator. Similarly, the service that prepares a data set for data integration can be provided by another service in the data flow network. The flexibility offered through the chaining and orchestration of distributed, loosely coupled web services is the architectural support for the building of agile data systems.
Data Wrapping
Quality Assurance
Homogenization and Integration
Integrated Data Set
The providers of observational, emission, and modeling data are distributed. The individual data sets will be funeled into the integrated HTAP data set. This data set transfer will be accomplished using standard data transfer protocols. Transfering the data from the provider to the user will include two additional observations for each data set, quality assurance and semantic transformation.
On the left the inputs from observations, emissions, and model data
Interoperability Standards for HTAP Integration
- Parameter Naming: CF Naming Concention for Chemicals - Textor
- Data format: netCDF CF and others
- Data Access: OGC Web Coverage Service, WCS Galeon
Identify providers and datasets relevant to HTAP
Integrate multi-sensory data into a coherent data systems
In order to accomplish the objectives set for the HTAP TF it is evident that it will require the System of Systems approach as envisioned by GEO. Both the modeling of the chemical constituents as well as the Earth observations used to document the hemispheric transport are being performed by individual autonomous projects and programs (Systems). A key function of the Task Force is to assess the contributions of the individual systems and then integrate those into a coherent assessment. Much of this interim report is in fact such an assessment of the current knowledge based on previous or past models and observations.
In the next, upcoming phase of HTAP is to actually integrate the existing modeling and observing systems such that their combination and fusion can yield a deeper and more robust understanding of HTAP. since this next phase will involve integration of multiple relevant data sets, comparison and evaluation of multiple models, as well as the reconciliation of the observations and models to create the new and deeper understanding . In order to execute this extensive integration, it will be necessary to conduct this integration using a generally accepted framework as well as accepted scientific methods. It is believed that the GEO architecture and the System of Systems is an attractive approach to HTAP integration.
The HTAP program can also be considered an early demonstration of the GEO concepts through its end to end approach. Both the atmospheric modeling, as well as the observations currently exist through the operation of existing modeling and observation systems. The Task Force has agreed organizing and evaluating those models, assembling and integrating the observational data sets and then reconciling the models with the observations will be the focus of the Phase II effort. The Task Force will also prepare and deliver a report to LRTP to aid its deliberations and its decision making processes. This sequence of activities constitutes an end to end approach that turns observations and models into actionable knowledge for societal decision making. One could say that this is an octagonal approach to more deliberate step by step development of GEOSS where in Phase I interoperability, in Phase II ???
Provider nodes
- Federated Data System DataFed
- NASA Data System Giovanni
- Emission Data System NEISGEI
- Juelich Data System
- AeorCom
- EMEP
Data Networks. Connected hubs; Show Core HTAP network
See 20 selected datasets in the federated data systems, DataFed
Perform QA at all steps
Reconciliation and Integration of Observations, Emissions and Models
Compare observations to models and emissions
Characterize pollutant pattern and SSR
Develop real-time data assimilation
Perform reanalysis with assimilated data
Organizational Aspects
HTAP Relationship to GEO and GEOSS
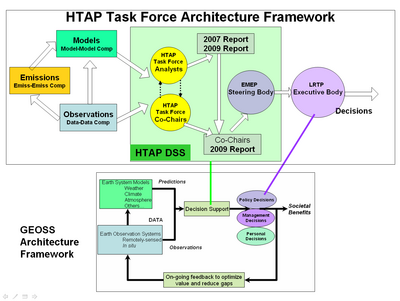
There is an outstanding opportunity to develop a mutually beneficial and supportive relationship between the activities of the HTAP Task Force and that of GEO. The Group of Earth Observations with its broad range of national and organizational members has developed a general architectural framework for turning Earth observations into societal benefits. The three main components of this architecture are models, and observations, which then feed into decision support systems used in a variety of societal decision making. This general framework is well suited as an architectural guide to the HTAP program. However, this framework lacks specific guidelines and implementation details that are needed for practical Earth observing and decision support systems.
The HTAP program provides an opportunity to extend the GEO framework with more detailed features that arise in specific HTAP application context. In case of HTAP, the major activities are shown in the architectural diagram of Figure ?? The HTAP modeling is conducted through global scale chemical transport models that simulate or forecast the atmospheric chemical composition as a consequence of natural and human induced emissions. The observations arise from satellite, ground-based and airborne observations of chemical constituents and their hemispheric transport. The decision support system consists of the scientists as members of the HTAP task force, and the task force co-chairs as the intermediaries between LRTP and the TF. (Terry, Andre this description of the HTAP DSS needs your help).
Representing the Decision Support System (DSS) for HTAP is an important aspect because it can guide the design and and implementation of the information system for the support of the DSS processes. A higher resolution DSS design document is also beneficial as a communications medium for the interacting system of systems. A domain specific DSS may also allow the generalization and applicability to the design of DSS structures for similar application domains.
The implementation of the GEO framework utilizes the concept of Global Observing System of Systems (GEOSS). Traditionally, Earth observations were performed by well defined systems such as specific satellites and monitoring networks which were designed and operated using systems engineering principles. However, GEO recognized that the understanding of Earth system requires the utilization and integration of the individual, autonomous systems. The key difference between the Systems and System of System approaches are highlighted in Table 1.
HTAP Relationship to IGACO
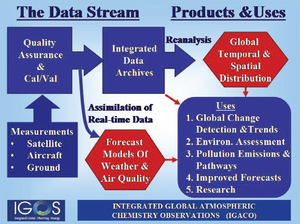
The HTAP program can also have a mutually beneficial interaction with the IGACO program. Integrated Global Atmospheric Chemistry Observations (IGACO) Theme is part of the Integrated Global Observing Strategy (IGOS). The IGACO program is formulated by an array of experienced atmospheric scientists. IGACO proposes a specific framework for the system components that processes the observational data and models. It also specifies the higher level information products that can be used for creating social benefit.
In the IGACO framework, the data products from satellite, surface, and aircraft observations are collected for inclusion into an integrated data archive. A key component in the IGACO data flow is the mandatory quality assurance and QA QC that precedes the archiving. This is particularly important for HTAP where multi-sensory data from many different providers are to be combined into an integrated database. In the IGACO framework, a key output from the data system is a high integrated spatial-temporal data set which can be used in a multitude of applications that produce socal benefit. The goal of creating such an integrated data set is shared by the IGACO and the HTAP programs (?? Len, this section could benefit from your input)
HTAP Relationship with Other Programs
--- ---