Difference between revisions of "Category:Documentation Connections"
| (75 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | == Introduction == | |
| + | |||
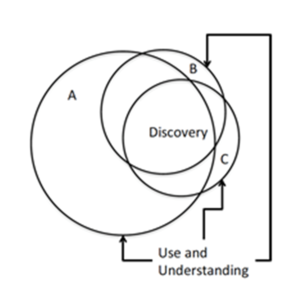
| + | [[File:Figure 1.png|thumb|Metadata Dialects|Schematic diagram of conceptual overlaps between three metadata dialects (A, B, and C). Note: More overlap is expected for discovery than for use and understanding concepts.]] | ||
| + | The ESIP Community supports a vast array of systems that are accessed and utilized by a diverse group of users. Historically, groups within the community have approached metadata differently in order to effectively describe their data. As a result, similar dialects have emerged to address specific user requirements. | ||
| + | The multi-dialect approach described above hinders interoperability— as it results in different terminology being used to describe the same concepts. By clearly depicting fundamental documentation needs and concepts and mapping to them in the different dialects, confusion is minimized and interoperability is facilitated. Thus, demonstrating connections between dialects increases discoverability, accessibility, and reusability of data via consistent, compatible metadata. | ||
| − | + | This document describes the connections between fundamental concepts in dialects used throughout the ESIP Community – such that effective communication is maintained even when different metadata models are employed. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | == Preface == | |
| − | + | The following pages are intended to help understand connections between metadata dialects in order to implement complete and consistent metadata. For convenience, this reference is divided into 5 major sections, consisting of: Introductory Material, Documentation Recommendations, Metadata Implementation, Documentation Selection Scenarios, and the Appendixes. Each of these sections is further divided into subsections. | |
| + | For your reference, a full table of contents is provide below. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Table of Contents == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Documentation Terminology]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Concepts Glossary]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Documentation Recommendations]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Metadata Dialects]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[:Category:Metadata Implementation|Metadata Implementation]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Documentation Selection Scenarios]] | ||
| + | |||
[[Category:Documentation Cluster]] | [[Category:Documentation Cluster]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:52, September 21, 2015
Introduction
The ESIP Community supports a vast array of systems that are accessed and utilized by a diverse group of users. Historically, groups within the community have approached metadata differently in order to effectively describe their data. As a result, similar dialects have emerged to address specific user requirements. The multi-dialect approach described above hinders interoperability— as it results in different terminology being used to describe the same concepts. By clearly depicting fundamental documentation needs and concepts and mapping to them in the different dialects, confusion is minimized and interoperability is facilitated. Thus, demonstrating connections between dialects increases discoverability, accessibility, and reusability of data via consistent, compatible metadata.
This document describes the connections between fundamental concepts in dialects used throughout the ESIP Community – such that effective communication is maintained even when different metadata models are employed.
Preface
The following pages are intended to help understand connections between metadata dialects in order to implement complete and consistent metadata. For convenience, this reference is divided into 5 major sections, consisting of: Introductory Material, Documentation Recommendations, Metadata Implementation, Documentation Selection Scenarios, and the Appendixes. Each of these sections is further divided into subsections. For your reference, a full table of contents is provide below.
Table of Contents
Pages in category "Documentation Connections"
The following 6 pages are in this category, out of 6 total.