WCS Access to netCDF Files
Wrapper software for WCS access to netCDF files
Background
The netCDF file format is a common way of storing gridded meteorological and air quality model results. The netCDF files that are also conformant with the CF convention further enhances the semantics of the netCDF files. Most of the recent model outputs are conformant with netCDF-CF.
The netCDF-CF convention facilitates the storage and transmission of model data sets using standard formats. The low level libraries provided by UNIDATA also provide a clear API for creating and accessing data from netCDF files.
Data access through OGC WCS protocol
The WCS protocol uses a physical coordinate system for accessing data, by explicitaly facilitating space-time queries using a geographic bounding box and a time-range to define the data access request. The purpose of this effort is to create a portable software template for accessing netCDF-formated data using the WCS protocol. Using that protocol will allow accessing the stored data by any WCS complient client software. It is hoped that the standards-based data access service will promote the development and use of distributed data processing and analysis tools.
Interoperability Work within HTAP TF
The adoption of a set of interoperability standards is a necessary condition for building an agile data system from loosely coupled components for HTAP. During 2006/2007, members of HTAP TF have made considerable progress in evaluating and selecting suitable standards. They also participated in the extension of several international standards, most notably standard names and a standard data query language.
The methods and tools for model inter comparisons was a subject of a productive workshop at JRC Ispra in March 2006. European and American members of the HTAP TF presented their respective approaches to model and data intercomparisons as part of their respective projects ENSEMBLES, Eurodelta, ACCENT, AEROCOM, GEMS, and DataFed. Several recommendations were made to improve future use of intercomparison data. The most important recommendation was to adopt a common data format, netCDF CF conventions and to develop a list of Standard Names.
The naming of individual chemical parameters will follow the CF convention used by the Climate and Forecast (CF) communities. The existing names for atmospheric chemicals in the CF convention were inadequate to accommodate all the parameters used in the HTAP modeling. in order to remedy this shortcoming the list of standard names was extended by the HTAP community under leadership of C. Textor. She also became a member of the CF convention board that is the custodian of the standard names. The standard names for HTAP models were developed using a collaborative wiki workspace. It should be noted, however, that at this time the CF naming convention has only been developed for the model parameters and not for the various observational parameters.(See Textor, need a better paragraph).
For modeling data, the use of netCDF-CF as a standard format is recommended. The use of a standard physical data format and the CF naming conventions allows, in principle, a semantically well-defined data transfer between data provider and consumer services. The netCDF CF data format is most useful for the exchange of multidimensional gridded model data. It was also demonstrated that the netCDF format is well suited for the encoding and transfer of station monitoring data. Traditionally, satellite data were encoded and transferred using the HDF format.
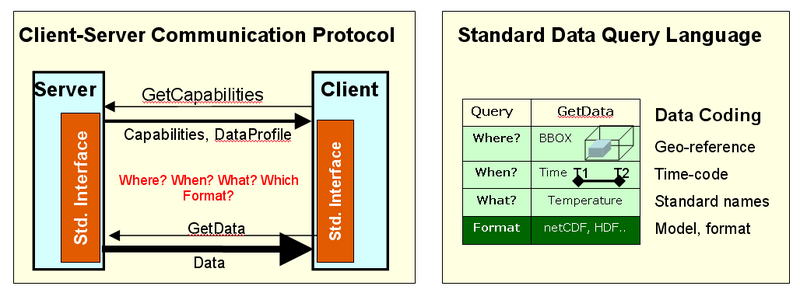
Figure 2. Interoperability protocols and standard query language
The third aspect of data interoperability is a standard data query language through which user services request specific data from the provider services. It is proposed that for the HTAP data information system adapts the Web Coverage Service (WCS) as the standard data query language. The WCS data access protocol is defined by the international Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC), which is also the key organization responsible for interoperability standards in GEOSS. Since the WCS protocol was originally developed for the GIS community, it was necessary to adapt it to the needs of "Fluid Earth Sciences". Members of the HTAP group have been actively participating in the adaptation and testing of the WCS interoperability standards.
Wrapper software description and instalation
The WCS protocol consists of three service calls:
- getCapabilities
- describeCoverage
- getCoverage
The purpose of the wrapper software is to respond to these three HTPP GET queries. The main query is getCoverage, which returns the requested data subset. The getCapabilities returns an XML file which lists the datasets offered by the server. The describeCoverage describes each data layer in more detail.
The WCS-netCDF wrapper software was developed for DataFed on a Windows .NET development platform. However, most other servers use the Linux operating system. For this reason, the WCS wrapper developed and tested for both Windows and Linux versions. In fact, test servers have been prepared for both platforms.
- Test server Windows platform (this will link to a live server)
- Test server Linux platform (this will link to a live server)
The main componenets of the wrapper software are shown schematically in the Figure below.
At the lowest level are open source libraries for accessing netCDF, XML files. At the next level are Python scripts for extracting spatially subset slices for specific parameters and times. At the third level, is the WCS interpreter that parses the WCS url. Administrative tools are also provided for creating the Capabilities and the Description documents.
The detailed instructions for the WCS wrapper software are maintained on a separate page, maintained by Kari Hoijarvi (kari@me.wustl.edu), 314 935 5772.