Difference between revisions of "EE CompliancePatternTrend"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Exceptional_Air_Pollution_Event_Analysis_Community_Workspace|< Back to Exceptional Event Workspace]]<br> | [[Exceptional_Air_Pollution_Event_Analysis_Community_Workspace|< Back to Exceptional Event Workspace]]<br> | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
| + | ==Definitions according to EE Rule == | ||
| + | (j) '''''Exceptional event''''' means an event that affects air quality, is not reasonably controllable or preventable, is an event caused by human activity that is unlikely to recur at a particular location or a natural event, and is determined by the Administrator in accordance with 40CFR 50.14 to be an exceptional event. It does not include stagnation of air masses or meteorological inversions, a meteorological event involving high temperatures or lack of precipitation, or air pollution relating to source noncompliance. | ||
| + | |||
| + | (k) '''''Natural event''''' means an event in which human activity plays little or no direct causal role. | ||
| + | |||
| + | (l) '''''Exceedance''''' with respect to a national ambient air quality standard means one occurrence of a measured or modeled concentration that exceeds the specified concentration level of such standard for the averaging period specified by the standard. | ||
| + | |||
==What is na Exceptional Event? (EE)== | ==What is na Exceptional Event? (EE)== | ||
Revision as of 14:19, November 12, 2007
< Back to Exceptional Event Workspace
Definitions according to EE Rule
(j) Exceptional event means an event that affects air quality, is not reasonably controllable or preventable, is an event caused by human activity that is unlikely to recur at a particular location or a natural event, and is determined by the Administrator in accordance with 40CFR 50.14 to be an exceptional event. It does not include stagnation of air masses or meteorological inversions, a meteorological event involving high temperatures or lack of precipitation, or air pollution relating to source noncompliance.
(k) Natural event means an event in which human activity plays little or no direct causal role.
(l) Exceedance with respect to a national ambient air quality standard means one occurrence of a measured or modeled concentration that exceeds the specified concentration level of such standard for the averaging period specified by the standard.
What is na Exceptional Event? (EE)
The Exceptional Events Rule requires states that flag data to satisfy the requirements of 40 CFR 50.14 (c)(3)(iii) to provide evidence that:
- The event satisfies the criteria that it was not reasonably controllable or preventable
- There would have been no exceedances or violation but for the event.
- Tthe event is associated with a measured value in excess of historical values
- There is a clear casual relationship between the measured value and the event
1. Not Reasonably Controllable or Preventable
2. No Exceedance or Violation But For the Exceptional Event
According to the EE Rule, observationas can be EE-flagged if the concentration exceeds the standard due to the exceptional event.
- The leftmost figure shows a case when the 'exceptional' concetration raises the level above the standard.
- In the next case, the concentration from controllable sources is sufficient cause the exceedance. Such an exceedance is not a 'but for' case and should not be flagged.
- In the third case, there is no exceedance, hence no justification for EE flag.
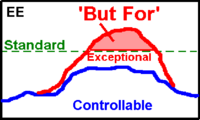
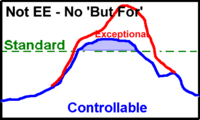
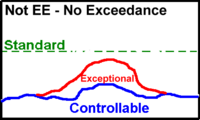
Illustration Exceptional Events, EE and non-EE events by the EE Rule.
3. The Event is in excess of the Historical Values
1999-2001
2000-2002
2001-2003
2002-2004
2003-2005
2004-2006
2005-2007

















