HTAP GEOSS
Relationship to GEO and GEOSS
There is an outstanding opportunity to develop a mutually beneficial and supportive relationship between the activities of the HTAP Task Force and that of the Group of Earth Observations (GEO). The national and organizational members of GEO have adapted a general architectural framework for turning Earth observations into societal benefits. The three main components of this architecture are models, and observations, which feed into decision support systems for a variety of societal decision making processes.
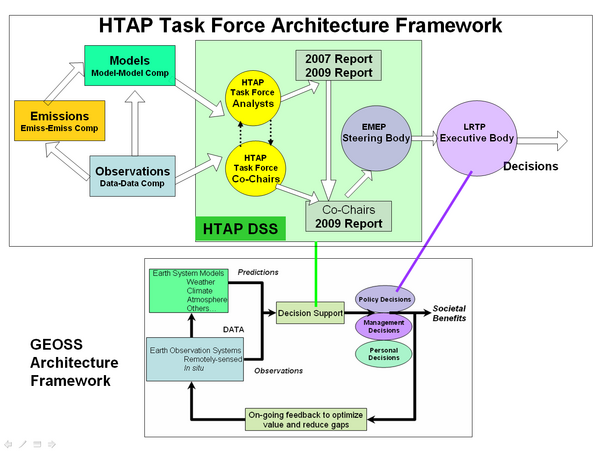
Figure 4. Architecture Framework for HTAP and GEOSS
This general GEO framework is well suited as an architectural guide to the HTAP program. However, it is void of specific guidelines and details that are needed for application areas such as HTAP. The HTAP program provides an opportunity to apply and extend the GEO framework. In case of HTAP, the major activities are shown in the architectural diagram of Figure 4. The modeling is conducted through global scale chemical transport models. The observations arise from satellite, ground-based and airborne observations of chemical constituents and their hemispheric transport. In case of HTAP, a third input data stream is needed for emissions which i neither observation, nor a model.
The HTAP decision support system consists primarily of humans. They need to be supported by an IT infrastructure and a set of enabling tools.
The first cluster is composed by the analysts who are the members of the HTAP task force. Their products are the 2007 and 2009 assessment reports submitted to the HTAP co-chairs and to EMEP. A second shorter report is prepared and submitted to the EMEP executive body, which is the decision making body of the LRTP convention. (Terry, Andre this description of the HTAP DSS needs your help).
Developing a higher resolution design chart for the HTAP DSS is an important task because it can guide the design and and implementation of the supporting information system. Furthermore, the detailed DSS architectural map may also serve as a communications channel for the interacting system of systems components. The insights gained in developing the HTAP DSS may also help the DSS design in similar applications.
The implementation of the GEO framework utilizes the concept of Global Observing System of Systems (GEOSS). Traditionally, Earth observations were performed by well defined systems such as specific satellites and monitoring networks which were designed and operated using systems engineering principles. However, GEO recognized that the understanding of Earth system requires the utilization and integration of the individual, autonomous systems.
While system science is a well developed engineering and scientific discipline, the understanding and development of System of Systems is in its infancy. The work of HTAP TF may provide an empirical testbed for the study of this new and promising integration architecture. Since, the HTAP TF activity encompasses virtually all aspects of GEOSS system of systems integration, it is an attractive "near-term opportunity" to demonstrate the GEOSS concept. An initial low-key demonstration could be accomplished as part of the HTAP TF 2009 assessment. Such a GEOSS demonstration is particularly timely since the data resources, data mediators and the connectivity infrastructure is nearly ready to be connected into a system of systems. Also, there are strong societal drivers to extend an update of LRTP convention to incorporate the air pollution impacts of one continent to another.
An HTAP-GEOSS demonstration would also demonstrate System of Systems approach not through stovepipe but through a dynamic network approach.
This sequence of activities constitutes an end to end approach that turns observations and models into actionable knowledge for societal decision making. One could say that this is an octagonal approach to more deliberate step by step development of GEOSS.